This is an old revision of the document!
ADP5589 - Microcontroller No-OS Driver
Supported Devices
Evaluation Boards
Overview
The ADP5589 a 19 channel GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) port expander with built-in keypad matrix decoder, programmable logic, reset logic, and PWM generator. The IC is capable of handling QWERTY size keyboards and GPIO expansion. I/O expander ICs are used in portable devices (phones, remote controls, & cameras) and non-portable applications (healthcare, industrial & instrumentation).
I/O expanders can be used to increase the number of I/Os available to a processor or to reduce the number of I/Os required through interface connectors for front panel designs.

The goal of this project (Microcontroller No-OS) is to be able to provide reference projects for lower end processors, which can't run Linux, or aren't running a specific operating system, to help those customers using microcontrollers with ADI parts. Here you can find a generic driver which can be used as a base for any microcontroller platform and also specific drivers for Renesas platforms.
HW Platform(s):
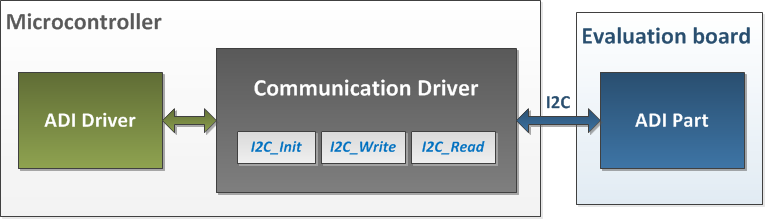
Driver Description
The driver contains two parts:
The driver for the ADP5589 part, which may be used, without modifications, with any microcontroller.
The Communication Driver, where the specific communication functions for the desired type of processor and communication protocol have to be implemented. This driver implements the communication with the device and hides the actual details of the communication protocol to the
ADI driver.
The Communication Driver has a standard interface, so the ADP5589 driver can be used exactly as it is provided.
There are three functions which are called by the ADP5589 driver:
I2C_Init() – initializes the communication peripheral.
I2C_Write() – writes data to the device.
I2C_Read() – reads data from the device.
The following functions are implemented in this version of ADP5589 driver:
| Function | Description |
| void ADP5589_SetRegisterValue(unsigned char registerAddress, unsigned char registerValue) | Writes data into a register. |
| unsigned char ADP5589_GetRegisterValue(unsigned char registerAddress) | Reads the value of a register. |
| unsigned char ADP5589_Init(void) | Initializes the communication peripheral and checks if the ADP5589 part is present. |
| void ADP5589_InitPwm(void) | Initializes the PWM generator in continuous mode. |
| void ADP5589_SetPwm(unsigned short pwmOffTime, unsigned short pwmOnTime) | Sets the PWM On and Off times. |
| void ADP5589_GpioDirection(unsigned char reg, unsigned char val) | Sets the direction of the pins. |
| unsigned char ADP5589_GetPinState(unsigned char reg) | Reads the state of the pins. |
| void ADP5589_InitKey(unsigned char pmodPort) | Initializes keyboard decoder. |
| unsigned char ADP5589_KeyDecode(unsigned char reg, unsigned char pmodPort) | Decodes the key pressed on the Pmod-KYPD. |
| void ADP5589_KeyLock(unsigned char pmodPort) | Locks the ADP5589 and requests Password for unlock. |
Downloads
Renesas RX62N Quick Start Guide
This section contains a description of the steps required to run the ADP5589 demonstration project on a Renesas RX62N platform.
Required Hardware
Required Software
Hardware Setup
A PmodIOXP has to be interfaced with the Renesas Demonstration Kit (RDK) for RX62N:
PmodIOXP J3 connector 1 (SCL) → YRDKRX62N J2 connector Pin 1
PmodIOXP J3 connector 3 (SDA) → YRDKRX62N J2 connector Pin 3
PmodIOXP J3 connector 5 (GND) → YRDKRX62N J8 connector Pin 4
PmodIOXP J3 connector 7 (VCC) → YRDKRX62N J8 connector Pin 3

Reference Project Overview
The reference project waits for a password to unlock the keypad.

After the keypad is unlocked the state of the pin R0 and the key presses are displayed on the LCD. Also the PWM generator is enabled on pin R3.

Software Project Setup
This section presents the steps for developing a software application that will run on the Renesas Demo Kit for RX62N for controlling and monitoring the operation of the ADI part.
Run the High-performance Embedded Workshop integrated development environment.
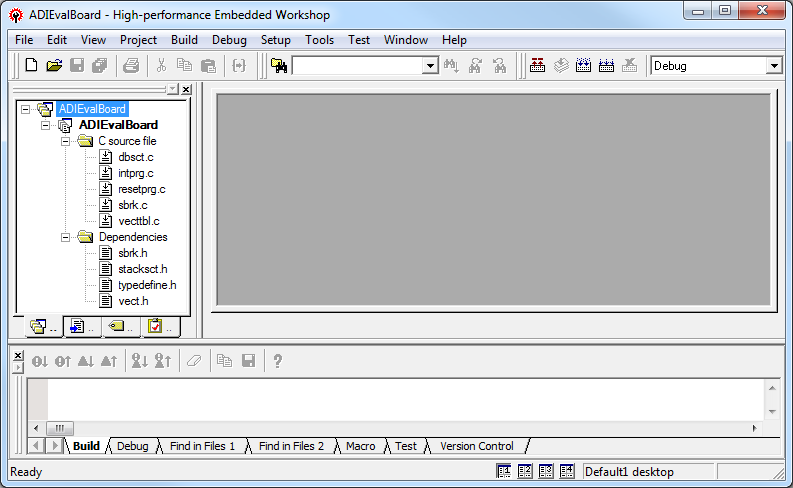
A window will appear asking to create or open project workspace. Choose “Create a new project workspace” option and press OK.
From “Project Types” option select “Application”, name the Workspace and the Project “ADIEvalBoard”, select the “RX” CPU family and “Renesas RX Standard” tool chain. Press OK.

The RPDL (Renesas Peripheral Driver Library) has to integrated in the project. Unzip the RPDL files (double-click on the file “RPDL_RX62N.exe”). Navigate to where the RPDL files were unpacked and double-click on the “Copy_RPDL_RX62N.bat” to start the copy process. Choose the LQFP package, type the full path where the project was created and after the files were copied, press any key to close the window.
The new source files have to be included in the project. Use the key sequence Alt, P, A to open the “Add files to project ‘ADIEvalBoard’” window. Double click on the RPDL folder. From the “Files of type” drop-down list, select “C source file (*.C)”. Select all of the files and press Add.

To avoid conflicts with standard project files remove the files “intprg.c” and “vecttbl.c” which are included in the project. Use the key sequence Alt, P, R to open the “Remove Project Files” window. Select the files, click on Remove and press OK.

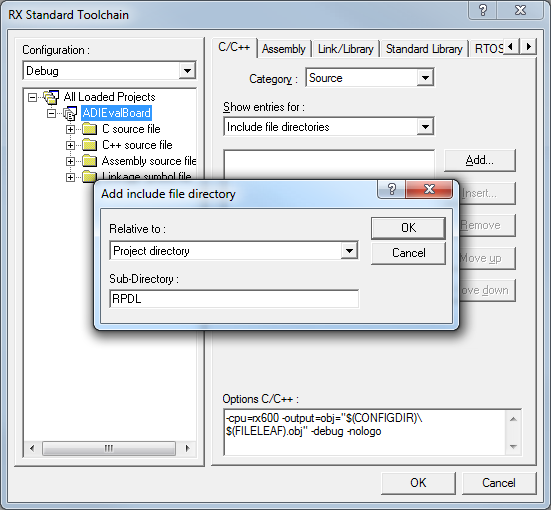
Next the new directory has to be included in the project. Use the key sequence Alt, B, R to open the “RX Standard Toolchain” window. Select the C/C++ tab, select “Show entries for: Include file directories” and press Add. Select “Relative to: Project directory”, type “RPDL” as sub-directory and press OK.
The library file path has to be added in the project. Select the Link/Library tab, select “Show entries for: Library files” and press Add. Select “Relative to: Project directory”, type “RPDL\RX62N_library” as file path and press OK.

Because the “intprg.c” file was removed the “PIntPrg” specified in option “start” has to be removed. Change “Category” to “Section”. Press “Edit”, select “PIntPRG” and press “Remove”. From this window the address of each section can be also modified. After all the changes are made press OK two times.

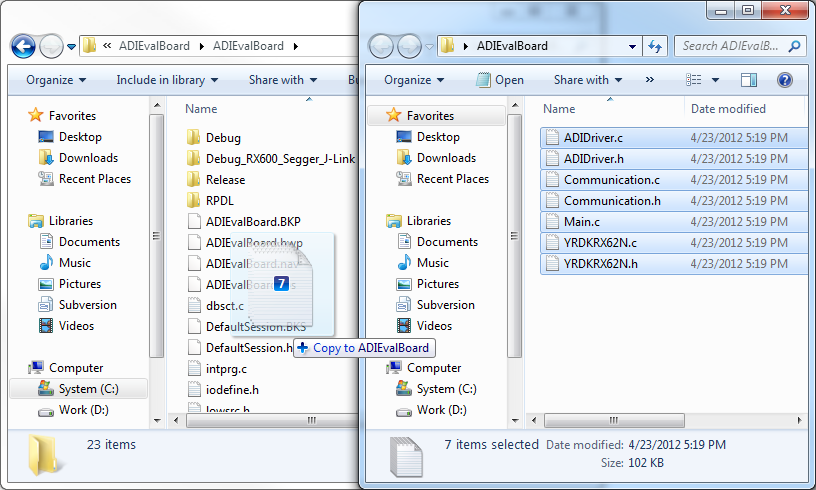
Now, the files have to be included in the project. Use the key sequence
Alt, P, A to open the “
Add files to project ‘ADIEvalBoard’” window. Navigate into
ADI folder. From the “
Files of type” drop-down list, select “
Project Files”. Select all the copied files and press
Add.

Now, the project is ready to be built. Press F7. The message after the Build Process is finished has to be “0 Errors, 0 Warnings”. To run the program on the board, you have to download the firmware into the microprocessor’s memory.
 This version (22 Mar 2012 08:20) was approved by Dragos Bogdan.
This version (22 Mar 2012 08:20) was approved by Dragos Bogdan.