 This version (03 Jan 2021 21:52) was approved by Robin Getz.The Previously approved version (06 May 2020 10:31) is available.
This version (03 Jan 2021 21:52) was approved by Robin Getz.The Previously approved version (06 May 2020 10:31) is available.
This is an old revision of the document!
The EVAL-ADL5902-ARDZ shield illustrates the functionality of the ADL5902, a 50 MHz to 9 GHz 65 dB TruPwr™ RMS responding RF power detector. The voltage outputs of the ADL5902 are routed to the ANALOG IN connector of the Arduino base board. This allows the RF power detector’s output voltage to be easily digitized and processed by the Arduino base board’s integrated six-channel ADC. The output of the ADL5902’s on-board temperature sensor is also routed to one of the ANALOG IN pins.
The power supply for the board comes from the Arduino base board through the POWER connector (5V). So while there is no need to connect an external power supply, the board can be powered by an external supply (6 Volt wall wart on P3 or 6V connected to the P1 screw terminals.
The EVAL-ADL5902-ARDZ is designed to work as a shield for EVAL-ADICUP3029 and DC2026C(also called Linduino One). For EVAL-ADICUP3029 , a PC software GUI application (EVAL-ADICUP3029) is available. Using this, the user can make RF power measurements and also calibrate the device to decrease measurement error. Device development drivers for EVAL-ADICUP3029 are also available, which the user may use to develop their own code for RF measurement, device calibration, and more.
Choose among the power option to Power up the EVAL-ADL5902-ARDZ by shorting the correct pins using the provided shorting jumper caps.
This works regardless of the connections on pin header P2
EVAL-ADL5902-ARDZ is already functional using this option, even without EVAL-ADICUP3029 or Linduino One
EVAL-ADL5902-ARDZ is already functional using this option, even without EVAL-ADICUP3029 or Linduino One
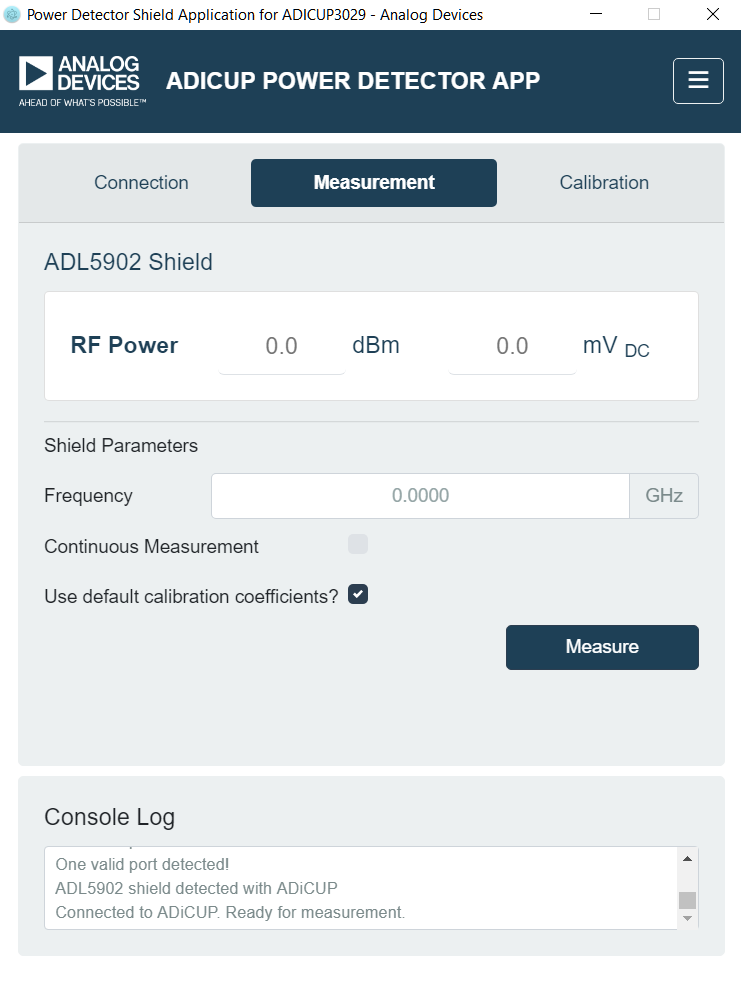
The EVAL-ADL5902-ARDZ shield converts the measured ADC code to RF input power in dBm using stored calibration coefficients. A 3-point calibration methodology is used. The software program includes default calibration coefficients that correspond to the default response of the ADL5902 across RF power level and frequency. datasheet specifications of ADL5902. Because of part-to-part device variation, observed accuracy using the default calibration coefficients will be sub-optimal. By availing of the software program's 3-point calibration function, measurement accuracy can be increased.
Related topic: Calibration of EVAL-ADL5902-ARDZ
Click “Connection” or “Calibration” to switch to respective window.
If you plan to operate at a frequency not on the list, make sure the calibrate at least on the adjacent upper and lower calibration frequencies (the software program will interpolate these data to ensure accuracy at the operating frequency. If the operating frequency is higher or lower than the available calibration frequencies, calibrate only on the highest or lowest calibration frequencies.
Calibration can be implemented using 2, 3 or 4-point calibration techniques which are used to approximate the transfer function of the ADL5902. Because the response of the ADL5902 changes with frequency, it is necessary to calibrate across frequency. If you are operating at a frequency that is in between two calibration frequencies, the software program will perform a weighted interpolation of the two sets of calibration coefficients.
The typical Vout vs. Pin characteristic of ADL5902 at 2.14GHz input is shown below (Figure 50 from the ADL5902 datasheet).
Figure 1. ADL5902 Characteristic Response at 2.14GHz
Two-point calibration is the simplest calibration technique. This models the transfer function of the ADL5902 and ADC as a single straight line
PIN = (CODE/SLOPE)+INTERCEPT
Where
PIN is the RF input power being measured
CODE is the ADC code
SLOPE is the slope of the ADL5902 transfer function's linear model (unit is LSBs/dB)
INTERCEPT is the (extrapolated) input RF power level which would yield and ADC code of 0 (this is a theoretical value with a unit of dBm)
SLOPE and INTERCEPT are calculated and stored during the calibration process by applying two known RF power levels, PIN1 and PIN2 (these RF power levels should be within the linear input range of the ADL5902) and measuring the corresponding ADC codes, CODE1 and CODE2. The equations for calculating SLOPE and INTERCEPT are as follows:
SLOPE = (CODE1–CODE2)/(PIN1−PIN2)
INTERCEPT = PIN1-(CODE1/SLOPE)
If there is some non-linearity in the transfer function of the RF detector, the number of calibration points can be increased to improve measurement accuracy. To implement three-point calibration, three known power levels are applied PIN1, PIN2 and PIN3 (PIN1 should be greater than PIN2 which should be greater than PIN3) and the corresponding ADC codes are noted (CODE1, CODE2, CODE3)
This results in two SLOPE values and two INTERCEPT values which are calculated using the equations
SLOPE1 = (CODE1–CODE2)/(PIN1−PIN2)
SLOPE2 = (CODE2–CODE3)/(PIN2−PIN3)
INTERCEPT1 = PIN1-(CODE1/SLOPE1)
INTERCEPT2 = PIN2-(CODE2/SLOPE2)
After calibration when measuring RF input power, the power is calculated using the appropriate equation
PIN = (CODE/SLOPE1)+INTERCEPT1 (if CODE > CODE2) or PIN = (CODE/SLOPE2)+INTERCEPT2 (if CODE < CODE2)
To decide which equation and calibration coefficients to use, the CODE from the ADC should be compared to CODE2 (CODE2 is the demarcation point between the two calibration regions). This will indicate which region of the ADL5902's transfer function the RF input power is located. For example, if the ADC CODE is greater than CODE2, this will indicate that the input power is greater than PIN2. So SLOPE1 and INTERCEPT1 should be used to calculate the input power. Because of the need to identify the region in which the measured RF input power is located, the CODE2 value should also be stored after calibration along with the SLOPE1, SLOPE2, INTERCEPT1 AND INTERCEPT2.
This technique can be extended to four or more calibration points. This may improve measurement accuracy at the cost of more complex calibration.
Development drivers are available for C and Python. Other development environments may be used but this development guided is focused on software development on CrossCore Embedded Studio (for C) and on Pycharm(for Python).
On the left side of the window, the structure of the loaded sample code should match the structure in the image shown below.
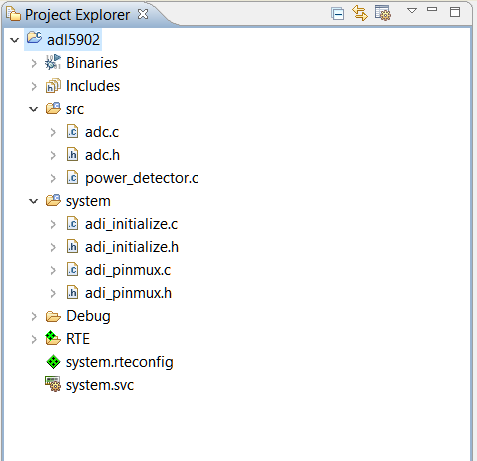
Assumes a fresh installation of all required software
EVAL-ADL5902-ARDZ Design Files
For any queries regarding the hardware and evaluation software, contact us at EngineerZone.